Mexico, with a population of 127,504,125, ranks as the 10th most populous country, just behind the Russian Federation. Located in North America, it covers 1,964,375 square kilometers, ranking 13th in the world, just below Saudi Arabia.
Mexico’s economic position in 2022 showcases a robust GDP of 1,465,854,089,286.47 USD, ranking it 14th globally. It follows closely behind Korea, with a GDP of 1,673,916,469,026.56 USD. In terms of GDP per capita, Mexico stands at 11,496.5229 USD, securing the 71st position worldwide.
It lags behind Maldives, with a GDP per capita of 11,780.8169 USD. Despite facing competition from these countries, Mexico’s economy remains significant on the global stage. Its per capita income is roughly one-third of the US. Mexico is classified as an upper-middle income country by the World Bank and a newly industrialized country by other organizations. This is while income distribution remains highly unequal.
More: Mexico’s economic system

Mexico’s economy has become increasingly oriented toward manufacturing and exports. It has a labor force of 53.74 million (2016) and it’s expected to become a fully industrial country in the next years.
Mexico is a mildly developed economy. The country is ranked 59th in the Index of Economic Freedom and 77th in the Human Development Index thus categorized as a moderately free country.
What are the economic activities of Mexico?
- Primary activities: 3.6% of GDP.
- Secondary activities: 31.9% of GDP.
- Tertiary activities: 64.5% of GDP.
Detailed composition of economic activities of Mexico
Primary Sector of Mexico

The economic activities in the primary sector of Mexico are diverse because of the diversity of climates in the country and its natural resources. Primary activities include agriculture, extracting minerals and other non-renewable resources, forestry, and fishing.
The primary sector in Mexico, particularly its agricultural activities, thrives due to its diverse climate and abundant natural resources. Approximately 49.96% of the country’s land is dedicated to agriculture. The main agricultural products include sugarcane, maize, milk, oranges, sorghum, tomatoes, chicken, wheat, chilies/peppers, and lemons/limes.
Despite contributing 3.6% to the GDP, agriculture plays a vital role in the economy. The variety of crops and animal products highlights the sector’s significance, providing sustenance, exports, and employment opportunities.
Even though agriculture accounts for a small percentage of Mexico’s GDP, many agricultural products are relevant to the economy. Mexico’s main agricultural products include sugar cane, corn, sorghum, wheat, oranges, bananas, tomatoes, lemons, poultry, milk, and eggs.
The country’s geological diversity provides a rich array of natural resources, including petroleum, silver, antimony, copper, gold, lead, zinc, natural gas, and timber. These resources play a crucial role in the economy, with petroleum being a major export and contributor to the GDP, while mining of metals like silver, copper, and gold also significantly impacts the country’s economy. Additionally, the abundance of natural gas and timber resources further supports various industries and sectors within the primary sector.
Furthermore, Mexico has huge reserves of non-renewable resources. its main extractions are oil, gold, silver, lead, copper, zinc, iron, coal, coke, iron, and manganese.
Mexico’s oil production of approximately 1.73 million barrels per day secures its position as the 8th largest oil producer globally. With reserves of 9.71 billion barrels, Mexico holds 0.35% of the world’s oil reserves, highlighting the country’s significant role in the global oil market.
Mexico’s natural gas production in 2020 reached 40 billion m³, ranking 21st globally, boosting the country’s economic activity.
Natural resources are owned by the nation, so the energy sector is managed by the government with limited private investment. Mexico is the 12th biggest oil producer (2.1 bbl/day). The biggest company in Mexico according to Fortune 500 is Pemex, state-owned oil and gas entity (98th in the world).
Secondary Sector of Mexico

What is the secondary sector or what are secondary activities?
The secondary sector encompasses industries that transform raw materials from primary activities into finished products for consumption. In Mexico, the main industrial products include food and beverages, tobacco, chemicals, iron and steel, petroleum, textiles, clothing, motor vehicles, and consumer durables.
However, the sectors driving the growth in Mexico’s industry are high-end manufacturing, such as automotive, plastics and aerospace industries.
Manufacturers play a crucial role in Mexico’s total exports, accounting for 78.19% in 2023. This highlights the significant contribution of the manufacturing sector to the country’s economy and trade balance.
Most of the success in the performance of Mexico’s economy relative to other major economies in Latin America is because of its thriving manufacturing sector. This sector has managed to grow thanks to its integration with the United States economy. Most of the industries are located in the northern cities of the country like Monterrey, Juarez, Mexicali, Ensenada, Nogales, Tecate and Tijuana.
The automotive industry stands out in the secondary sector. This sector has been experiencing double-digit growth in exports every year since 2010. It is recognized worldwide due to its high-quality standards. The automotive industry plays an important role in the Mexican economy. This sector is strategic because of its contribution to the GDP and because it is highly demanding of skilled labor, the multiplier effect on the supplying branches, and the sales of intermediate goods.
Tertiary sector of Mexico

What is the tertiary sector or what are tertiary activities?
The most important activities in the tertiary or service sector in Mexico are commerce, tourism, real estate, transportation and storage, telecommunications, and educational services. These activities play a crucial role in driving the country’s economy and meeting the diverse needs of its population.
The tertiary sector in Mexico encompasses a wide range of services where individuals provide knowledge and expertise to enhance productivity and meet various needs. This sector includes intangible goods like advice, attention, and expertise, catering to both consumers and businesses.
Notably, Mexico’s economy heavily relies on tourism, with 97,406,000 annual arrivals contributing significantly to its GDP. Cancun’s pristine beaches and Mayan ruins, along with Mexico City’s vibrant culture and historical sites, make them the most popular destinations, attracting tourists worldwide. With a tourist arrival ratio of 0.7639 per capita, the industry plays a crucial role in the country’s economic growth. The tourism sector is the fourth largest source of income for the country, Mexico is the top tourist destination in Latin America and the eighth most visited country in the world (with more than 20 million tourists per year).
Another example of tertiary economic activity is the mobile cellular sector, boasting approximately 128 million subscriptions, which fosters technological growth by enhancing
The financial services sector is dominated by foreign companies or the fusion of local and foreign banks, except Banorte. The banking system is profitable, liquid, and well-capitalized, but The sector suffers from concentration and conglomeration.
International trade of Mexico
Mexico is the 10th largest exporter in the world. In 2015, Mexico exported $391 billion and imported $377 billion, resulting in a positive trade balance of $14.4 billion. Mexico has free trade agreements with 46 countries, putting more than 90% of its trade under free trade agreements. Its main trade partners are the United States, Canada, China, Japan, South Korea, and Germany.
The main exports of Mexico are cars ($34.5 billion), vehicle parts ($25.6 billion), delivery trucks ($23.2 billion), computers ($20.9 billion) and crude petroleum ($19.4 billion). The main imports from Mexico are vehicle parts ($23.4 billion), refined petroleum ($18.5 billion), integrated circuits ($13.8 billion), computers ($10.3 billion) and cars ($9.5 billion).
Export Activities of Mexico
Mexico’s export activities are of high importance, accounting for 42.64% of its GDP in 2023, totaling 5.93E+11. This demonstrates a significant reliance on international trade for economic growth.

Mexico primarily exports cars, computers, vehicle parts, crude petroleum, and trucks. Its main export partner is the US, accounting for 77% of exports, followed by Canada, China, Taiwan, and South Korea.

Top imports from Mexico
Mexico’s import activities are of high importance, accounting for 45.47% of its GDP in 2023, totaling 5.98 quadrillion.
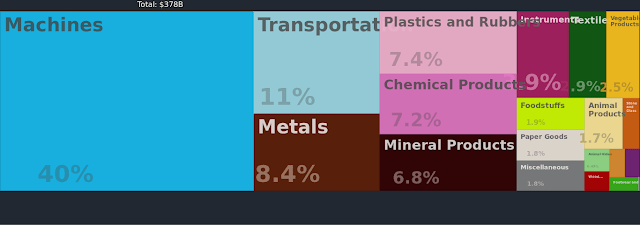
Mexico’s import activities are diverse, with the US being the largest partner at 56%, followed by China at 17%. Imports include refined petroleum, vehicle parts, machine parts, integrated circuits, and natural gas. Other key partners are Germany, South Korea, and Japan.
Mexico economy challenges in 2024
In 2024, Mexico faces challenges of income inequality, corruption, and cartel-based violence despite its upper-middle income status. The country’s tight monetary policy has helped decrease inflation, but state intervention in energy and infrastructure projects remains a concern. Mexico’s close ties with the US through trade and manufacturing have kept unemployment low, but social issues continue to hinder progress.
Sources:




Leave a Reply